Kubernetes service discovery in SonataFlow Operator
The Kubernetes service discovery allows you to describe the Kubernetes resource you want to perform HTTP requests on using a custom URI. Under the hood, it will discover the network endpoint (URL) to where to make the request.
The service discovery occurs during the operator managed deployment of a workflow, or during the application startup if you are using a standalone Quarkus Workflow Project. In both cases, this feature scans all the Quarkus configurations in search of the URI pattern. Therefore, you must remember that if the application startup time matters, consider using a known static URL instead.
Following is the custom URI pattern in Kubernetes service discovery:
kubernetes:<kind>.<version>.<group>/<namespace>/<resourceName>?<attributeName>=<attributeValue>
\________/ \____/ \_______/ \_____/ \_________/ \____________/ \______________________________/
scheme kind version group namespace resourceName additional resource attributes
\____________________/ \__________________________/
GVK Supported values:
- port=<PORT_NAME>
- label-name1=label-value1
- label-name2=label-value2The following scheme values are supported in the URI pattern:
-
kubernetes -
openshift -
knative
The following resources are supported for the Kubernetes GVK (Group, Version, and Kind):
-
services.v1 -
services.v1.serving.knative.dev -
pods.v1 -
deployments.v1.apps -
deploymentconfigs.v1.apps.openshift.io -
statefulsets.v1.apps -
routes.v1.route.openshift.io -
ingresses.v1.networking.k8s.io
|
When using The above URI looks directly for services.v1.serving.knative.dev resource. |
|
The |
- Query parameters in URI
-
Also known as query string. The query parameters are defined the similar way with URLs to assign value to specific attributes.
The following query parameters help the engine to be more precise when querying for a given Kubernetes resource:
-
Custom labels: The custom labels are used to filter services in case there are more than one service with the same label selector but exposing different ports. In this case, you can instruct the engine that if more than one service is found, then the engine must use the service containing the provided label.
The label is defined with the following expression and in case of multiple labels, you can use ampersand (&):
label-name1=label-value1&label-name2=label-value2Example label definition in URIkubernetes:pods.v1/<namespace>/<pod-name>?tier=backendUsing the previous URI example, if there are more than one service exposing the given pod, the
tier=backendlabel is used to filter the service. If the label does not exist, the first found service is used. -
Custom port: The custom
portis used to determine which port to use when multiple ports are configured in the target service. You can configure the port name to be queried using the following pattern:port=<PORT_NAME>
-
|
When you work with operator managed workflow deployments, there is no specific configuration required for the Kubernetes service discovery except by using the expected URI pattern. |
Kubernetes service discovery resolution
Based on the resource to be discovered, the Kubernetes service discovery follows specific paths as shown in the following figure:
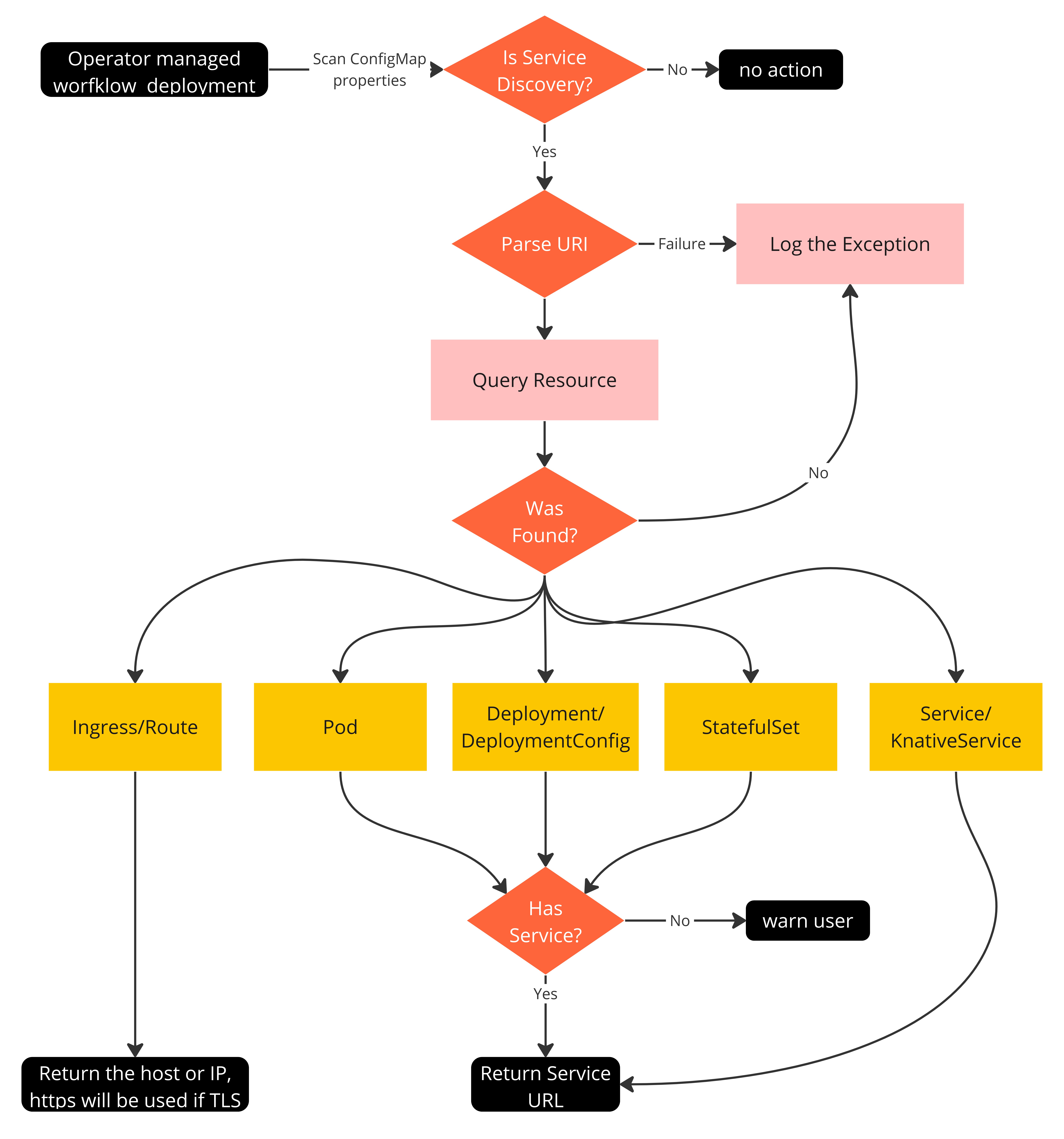
Example of Kubernetes service discovery in SonataFlow Operator
The Kubernetes service discovery is performed by the operator at workflow deployment time. At this point, the operator scans the workflow configuration parameters in the associated ConfigMap, and searches for the Kubernetes URI pattern. If the URI pattern is found, the operator parses the URI, queries the Kubernetes API searching for the given resource, and overrides the given parameter with the resolved value by adding an entry in the corresponding managed properties ConfigMap.
For example, consider a workflow with the name mortgage-workflow that consumes a resource running on Kubernetes to execute financial operations implemented by the Knative Service financial-service.
kind: ConfigMap
apiVersion: v1
metadata:
name: mortgage-workflow-props
namespace: example
labels:
app: mortgage-workflow
sonataflow.org/workflow-app: mortgage-workflow
data:
application.properties: >+
# service discovery configuration to resolve the financial-service
quarkus.rest-client.financial_service_yaml.url=${knative:services.v1.serving.knative.dev/financial-service}
|
Finally, as part of the deployment procedure the operator will create the following mortgage-workflow-managed-props ConfigMap, that contains all the configurations that are managed by the operator, including the service discovery properties that were calculated for the configuration above.
kind: ConfigMap
apiVersion: v1
metadata:
name: mortgage-workflow-managed-props
namespace: example
labels:
app: mortgage-workflow
sonataflow.org/workflow-app: mortgage-workflow
data:
application-dev.properties: >
org.kie.kogito.addons.discovery.knative\:services.v1.serving.knative.dev\/financial-service
= http://financial-service.example.svc.cluster.local
quarkus.rest-client.financial_service_yaml.url =
http://financial-service.example.svc.cluster.local
quarkus.http.port = 8080
quarkus.http.host = 0.0.0.0
... other operator calculated propertiesAs you can see, the service discovery URI ${knative:services.v1.serving.knative.dev/financial-service} was resolved to the URL http://financial-service.example.svc.cluster.local.
|
|
The |
Found an issue?
If you find an issue or any misleading information, please feel free to report it here. We really appreciate it!